
- #Mac information in a layer 2 frame is intended for which osi layer? registration
- #Mac information in a layer 2 frame is intended for which osi layer? Bluetooth
- #Mac information in a layer 2 frame is intended for which osi layer? mac
In our example, we have two VLANs, an orange VLAN and a blue VLAN.
#Mac information in a layer 2 frame is intended for which osi layer? mac
The switch we've build is in the MAC address table for separate VLANs. So even for broadcast messages the report in a different VLAN will not received a broadcast message. In the case of virtual LAN or VLAN the switch offers the capability to configure the ports into separate broadcast domains. When the MAC address is unknown the switch will behave like a hub and sends out that frame as a broadcast message so that it could learn which MAC address is reachable out of which port to build that MAC address table. Say if we move the host around, or if we plug into new hosts. Also the MAC address table even after it's built needs to have a time limit.

However, this MAC address table that the switch builds and learns needs to be built initially when none of the MAC addresses is known. In this case, if A is sending information toward B because the switch knows the MAC addresses of D you would just forward the frame out to the D port instead of flooding out to all the other ports. It builds a MAC address table inside and populates that table with the MAC addresses reachable out of each port. Nowadays, we typically connect the devices to a switch which act as a buffer between all the nodes. The hub is obviously an inefficient way to transmit data. B and C would check the data and simply drop it because it is not intended for them. In our example, if A once your transmit data frame intended for B the hub was still transmit the data frames to B and C. With a hub traffic coming in from any port is replicated by the hub and transmit it to all the other ports. In the early days, we typically used a device called a hub to connect these nodes. In order for the nodes on the land to reach each other the data needs to be transmitted from the source to the destination. Ethernet uses the MAC address as the address to identify each source and destination. Referring to the OSI model, this is a layer two level. The dominant technology in LAN today is Ethernet. These nodes could be laptops, computers, smartphones, or printers. A local area network is typically a single network where the nodes could reach each other. In modern local area networks We usually have a bus topology where the nodes are connected physically to the wire with each other. Many times we could refer to it as the burned-in address, the hardware address, or physical address. Because of its uniquely identifiable address and they're not easily changed, the MAC address has many other names.
#Mac information in a layer 2 frame is intended for which osi layer? Bluetooth
So on a computer with Ethernet, Wi-Fi, and Bluetooth interfaces, each of them should have a uniquely identifiable MAC address. Each of the interface should have a MAC address to uniquely identify yourself.
#Mac information in a layer 2 frame is intended for which osi layer? registration
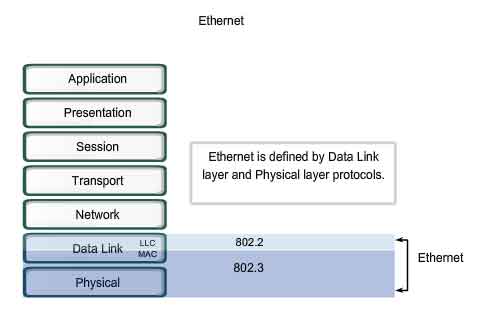
It is a number of purchase from IEEE registration authority. The first 24 bit of the MAC address consists of the OUI or organizationally unique identifier. Each group consists of two hexadecimal units. It is 48 bits in length and typically expressed in a group of six. The MAC address is a unique identifier assigned to a network interface CAD to uniquely identify the narrower interface it is assigned to. I would encourage you to take a look at the Wikipedia patient OSI model, if you're interested in learning more about it. Of course, this is the overgeneralization of the OSI model. The transport layer is when we talk about reliable and unreliable transmission of data segments such as TCP and UDP protocols. When we talk about IP addresses and routings later in this course, they're generally residing at layer three. The network layer governs the structure and transfer units of packets. The data link layer handles the data frames between two nodes. They usually involve things that we can see and touch. The physical layer includes the physical mediums such as fiber optics, coaxial, and twisted pair cables. For network engineers, we're typically working from the physical to the transport layer. For us we typically refer to the bottom as number one and gradually increase up to layer seven. From the bottom up their physical, data link, network, transport, session, presentation, and application. It breaks the technologies into seven layers each built on top of each other. According to Wikipedia the OSI model is a conceptual model that categorizes and standardizes the communication functions of a telecommunication or a computing system without regards to his underlying structure and technology. OSI stands for Open System Interconnection. The OSI model is a good way to normalize different technologies and group functionally similar technologies into the same category. When we talk about networking many times we will refer the technology or tools in reference the OSI layer. In this section, let's talk about MAC addresses and VLANs.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
